Care Programme
DETOXIFICATION
Detoxification, as reviewed here, is the constellation of physiological and psychological processes through which the body identifies, neutralizes, and eliminates toxic substances, metabolic byproducts, habits, and patterns. Alcohol and other narcotic withdrawal therapies are serious medical conditions requiring close supervision and are not discussed here.

REJUVENATION
Rejuvenation is a medical discipline focused on the practical reversal of the aging process.
Rejuvenation is distinct from life extension. Life extension strategies often study the causes of aging and try to oppose those causes in order to slow aging. Rejuvenation is the reversal of aging and thus requires a different strategy, namely repair of the damage that is associated with aging or replacement of damaged tissue with new tissue. Rejuvenation can be a means of life extension, but most life extension strategies do not involve rejuvenation.

WEIGHT LOSS
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue. Weight loss can either occur unintentionally due to malnourishment or an underlying disease or arise from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. “Unexplained” weight loss that is not caused by reduction in calorific intake or exercise is called cachexia and may be a symptom of a serious medical condition. Intentional weight loss is commonly referred to as slimming.

WEIGHT GAIN
Weight gain is an increase in body weight. This can involve an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits,
excess fluids such as water or other factors. Weight gain can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.

ANTI-AGING
Anti-aging creams are predominantly moisturiser-based cosmeceutical skin care products marketed with the promise of making the consumer look younger by reducing, masking or preventing signs of skin aging. These signs are laxity (sagging), rhytids (wrinkles), and photoaging, which includes erythema (redness), dyspigmentation (brown discolorations), solar elastosis (yellowing), keratoses (abnormal growths), and poor texture.

DE-STRESS
Stress is the body’s method of reacting to a condition such as a threat, challenge or physical and psychological barrier. Stimuli that alter an organism’s environment are responded to by multiple systems in the body. In humans and most mammals, the autonomic nervous system and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis are the two major systems that respond to stress.

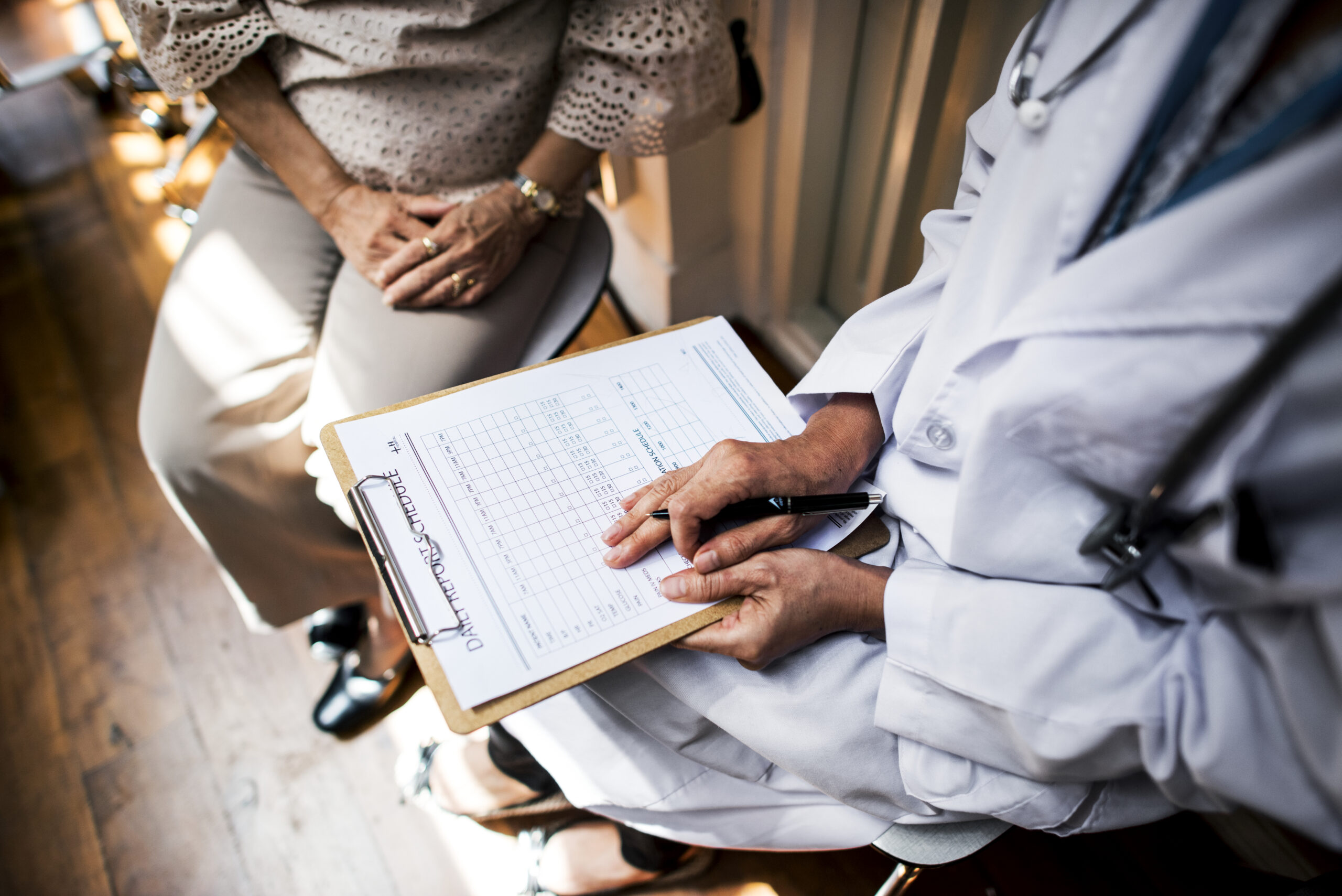
CONSTITUTIONAL ANALYSIS
Generally, they are very nonspecific, with a vast number of diseases and conditions as potential cause, which therefore require further evaluation for any diagnosis.
Examples include weight loss, fevers, headache, fevers of unknown origin, hyperhidrosis, generalized hyperhidrosis, chronic pain, fatigue, dyspnea, and malaise.
PULSE DIAGNOSIS
Pulse diagnosis is based on another microsystem with internal organs represented on the wrists. Once the Chinese doctor has questioned the patient and looked at the tongue, it is time for pulse diagnosis. The patient stretches out his wrists or lays them on a small oblong rice cushion on the table. The doctor will use three fingers to take the patient’s pulse at three positions on each wrist simultaneously, and will judge the pulse according to 28 variables . He will first use only light pressure against the patient’s wrist, then increase it. The light pressure allows the doctor to check one specific organ, the increased pressure another one. Every organ’s status can be monitored by the quality of the pulse. The doctor can, among other things, feel if the organ lacks energy, or the energy has stagnated, if there is a lack of ‘blood’, or if a pathogenic factor has invaded the organ.

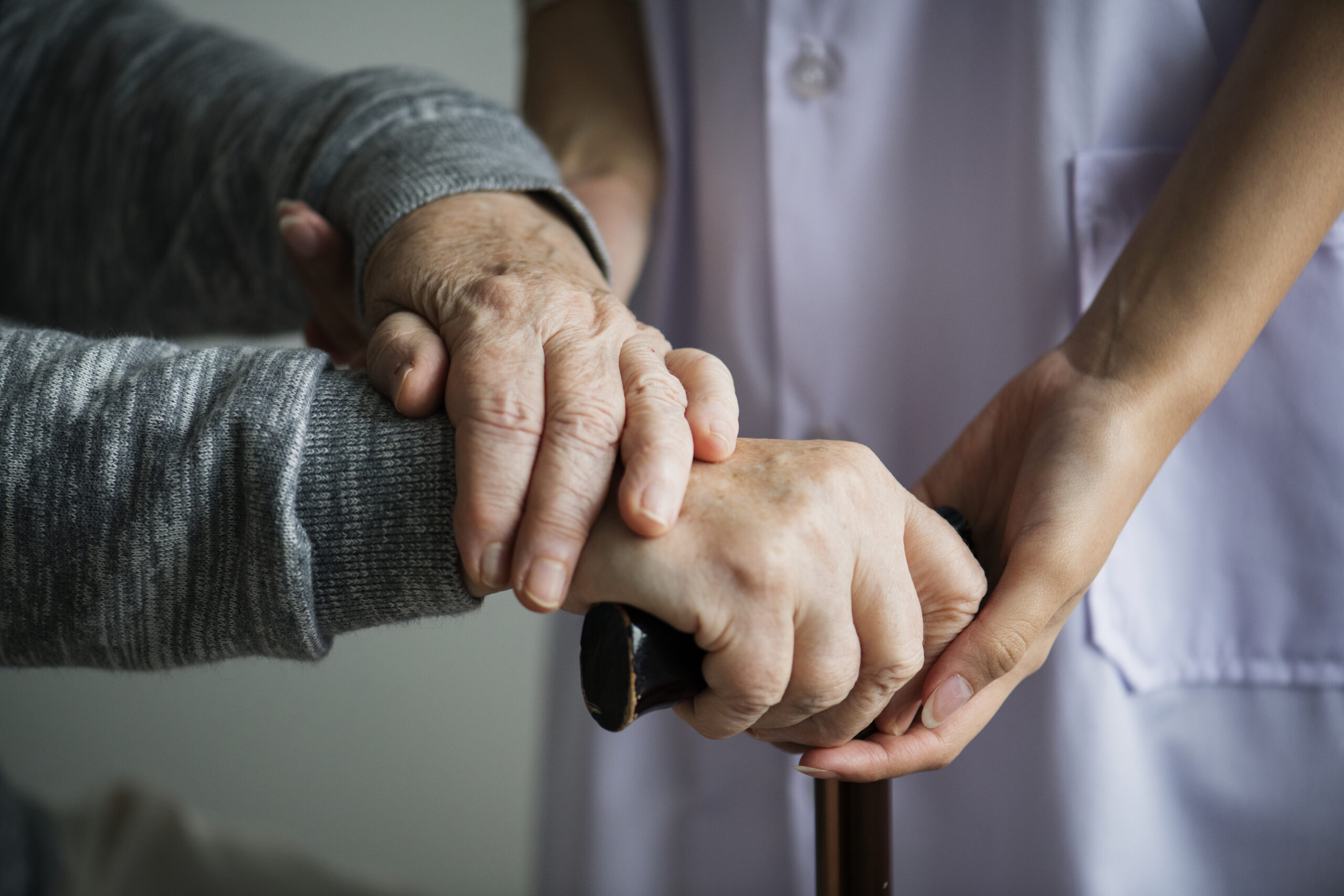
Geriatric care
Geriatric care management is the process of planning and coordinating care of the elderly and others with physical and/or mental impairments to meet their long term care needs, improve their quality of life, and maintain their independence for as long as possible. It entails working with persons of old age and their families in managing, rendering and referring various types of health and social care services. Geriatric care managers accomplish this by combining a working knowledge of health and psychology, human development, family dynamics, public and private resources as well as funding sources, while advocating for their clients throughout the continuum of care. For example, they may assist families of older adults and others with chronic needs such as those suffering from Alzheimer’s disease or other dementia.

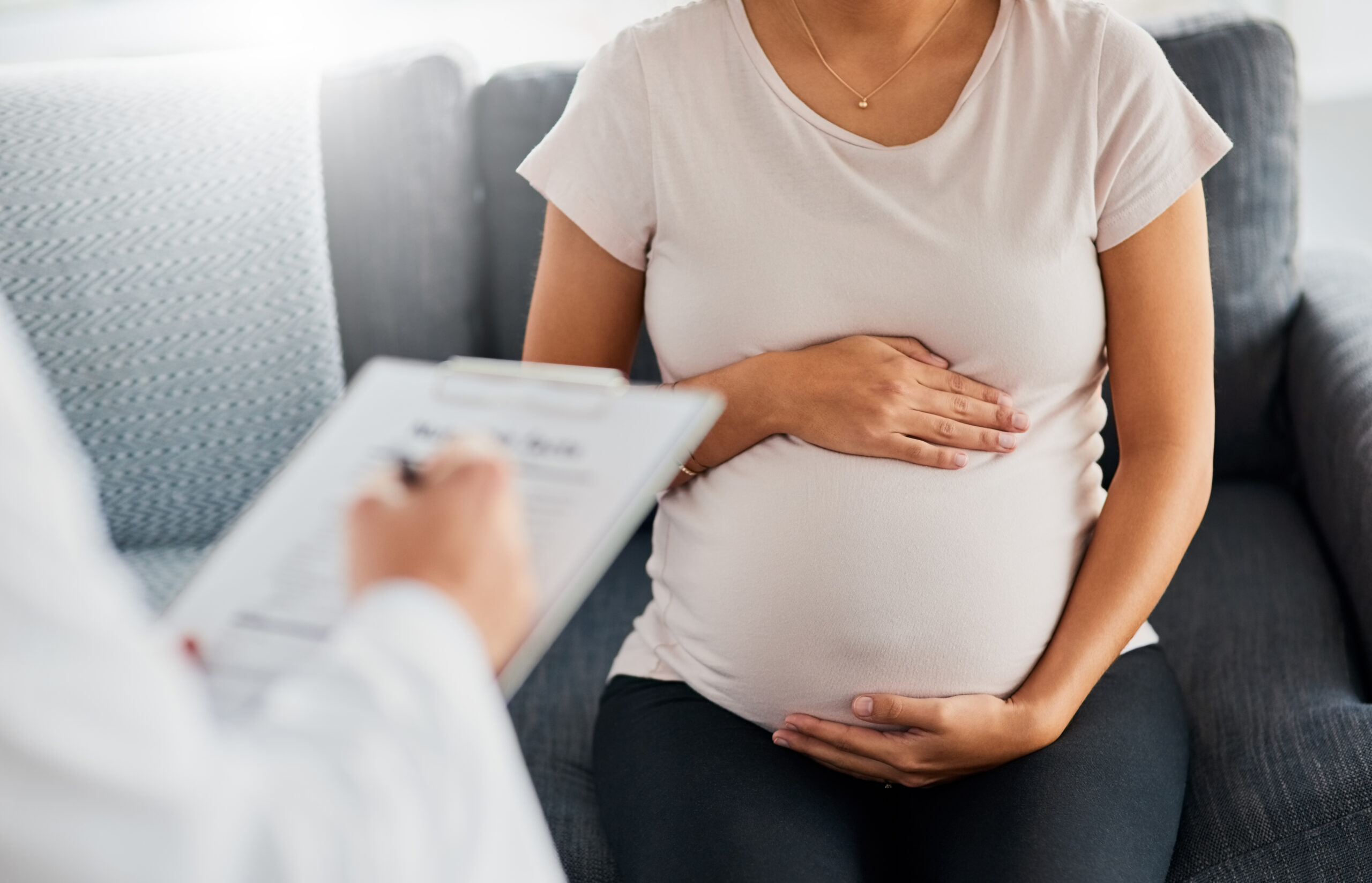
PRE-CONCEPTUAL COUNSELLING
Pre-conception counseling (also called pre-conceptual counseling) is a meeting with a health-care professional (generally a physician or midwife) by a woman before attempting to become pregnant. It generally includes a pre-conception risk assessment for any potential complications of pregnancy as well as modifications of risk factors, such as increasing folic acid intake to reduce the risk of neural tube defects and counseling on smoking cessation, alcohol reduction, and medications that may compromise fetal development.[1] Physicians, midwives and baby experts recommend that a woman visit them as soon as the woman is contemplating having a child, and optimally around 3 to 6 months before actual attempts are made to conceive.[2] This time frame allows a woman to better prepare her body for successful conception (fertilization) and pregnancy, and allows her to reduce any health risks which are within her control. Agencies such as the March of Dimes[3] have developed screening tools that healthcare providers can use with their patients. In addition, obstetricians or midwives (see Obstetrics, Midwifery, General Practitioner) have developed comprehensive check-lists and assessments for the woman who is planning to become pregnant.

ANTE-NATAL DETRY & LIFESTYLE REGIMEN
Antenatal care (ANC) coverage is a success story in Africa, since over two-thirds of pregnant women (69 percent) have at least one ANC contact. However, toachieve the full life-saving potential that ANC promises for women and babies,
four visits providing essential evidence based interventions – a package oftencalled focused antenatal care – are required. Essential interventions in ANCinclude identification and management of obstetric complications such as preeclampsia,tetanus toxoid immunisation, intermittent preventive treatment formalaria during pregnancy (IPTp), and identification and management ofinfections including HIV, syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).

CARE PROGRAMME GALLERY




